https://github.com/dataiku-research/cardinal
Tip revision: a28386b0de6d24c1a71d6585398fa7b2ce94f242 authored by Alexandre Abraham on 14 April 2021, 09:30:43 UTC
Add second example
Add second example
Tip revision: a28386b
README.md
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dataiku-research/cardinal/master/doc/_static/cardinal.png" width="300">
## Introduction
cardinal is a Python package to perform and monitor Active Learning experiments
leveraging various query sampling methods and metrics.
The project is currently maintained by [Dataiku's](https://www.dataiku.com/) research team.
## Getting started
Cardinal extensive [documentation](https://dataiku-research.github.io/cardinal/) features some examples helping you getting started with Active Learning:
* [Lowest confidence vs. Random sampling](https://dataiku-research.github.io/cardinal/auto_examples/plot_random_vs_confidence.html) presents a basic active learning pipeline and explains why it is better than random
* [Lowest confidence vs. KMeans sampling](https://dataiku-research.github.io/cardinal/auto_examples/plot_confidence_vs_diversity.html) presents more advanced techniques
* [Active learning on digit recognition and metrics](https://dataiku-research.github.io/cardinal/auto_examples/plot_digits_metrics.html) presents an experiment on MNIST dataset and proposes some metrics to estimate the accuracy uplift during an experiment
## Active Learning
Active Learning aims at optimizing the labeling of unlabeled samples at a given cost.
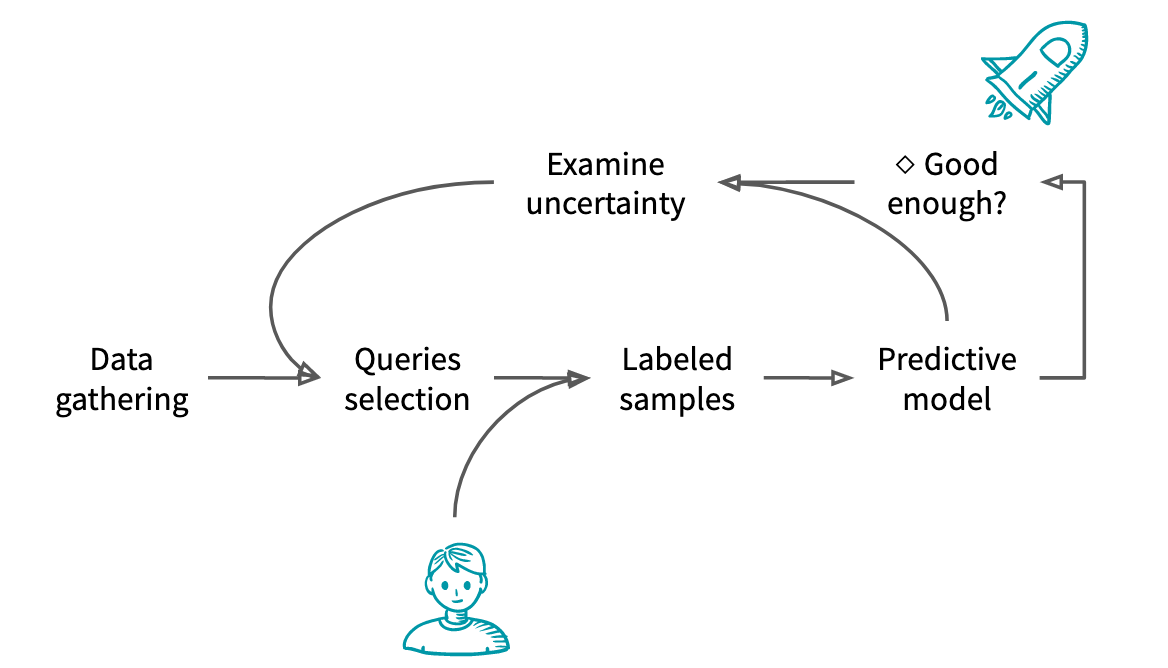
The typical Active Learning workflow is as follows:
* Unlabeled data is gathered
* From these unlabeled data, the experimenter selects samples to annotate
* The samples are given to an oracle that label them
* A model is trained based on the new and previous labels
* If the model is considered good enough or if there is no more budget, the model is shipped to production
* Otherwise, the experimenter uses knowledge about the model to select the next samples to annotate
The main challenges in Active Learning are:
* **Extracting information from the model.** The method can change depending on the model and the use case.
* **Selecting multiple samples at once.** It is unrealistic to assume that the model can be re-trained after
each labeling.
* **Make the most out of unlabeled information.** In the active learning setting, the experimenter is usually
faced with a large amount of unlabeled data compared to the labeling capacities.
## Taking off with cardinal
Let `X_unlabeled` be the pool of unlabeled data to be labeled and `(X_labeled, y_labeled)` the original labeled data to train our model.
One iteration of Active Learning can be written as:
```python
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from cardinal.uncertainty import ConfidenceSampler
model = RandomForestClassifier()
batch_size = 20
sampler = ConfidenceSampler(model, batch_size)
model.fit(X_labelled, y_labelled)
sampler.fit(X_labelled, y_labelled)
selected = sampler.select_samples(X_unlabelled)
#Updating the labeled and unlabeled pool
X_labelled = np.concatenate([X_labelled, selected])
#The selected samples are sent to be labeled as y_selected
y_labelled = np.concatenate([y_labelled, y_selected])
```
But how to evaluate the performance of the Active Learning process ?
Active Learning comes in two flavors: with *fixed testing set* and with *incremental testing set*. The former is almost always the only one proposed in the fixed environement of the Active Learning literature while the latter is most common in the wild.
* In the *fixed testing set*, there is already a large enough and representative testing set for the task at hand. This corresponds to the situation where a model has already been trained and tested, perhaps even deployed. As new data comes in, the machine learning practitioner can both score it with the existing model or manually label it. The same testing set will be used to evaluate potential additional performance gain.
Let `(X_test, y_test)` denote the fixed testing set. The above then becomes:
```python
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from cardinal.uncertainty import ConfidenceSampler
model = RandomForestClassifier()
batch_size = 20
sampler = ConfidenceSampler(model, batch_size)
accuracies = []
model.fit(X_labelled, y_labelled)
sampler.fit(X_labelled, y_labelled)
selected = sampler.select_samples(X_unlabelled)
# Evaluating performance
accuracies.append(model.score(X_test, y_test))
# Updating the labeled and unlabeled pool
X_labelled = np.concatenate([X_labelled, selected])
# The selected samples are sent to be labeled as y_selected
y_labelled = np.concatenate([y_labelled, y_selected])
```
* When starting a new machine learning project and data has to be collected and labeled, we are in the *incremental testing set* settings. There is no ground truth labelled set to start with and part of the new labeled data will make the testing set at each labeling iteration.
This is the corresponding Active Learning iteration:
```python
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from cardinal.uncertainty import ConfidenceSampler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
model = RandomForestClassifier()
batch_size = 20
sampler = ConfidenceSampler(model, batch_size)
accuracies = []
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_labelled, y_labelled, test_size=0.2, random_state=123)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
sampler.fit(X_train, y_train)
selected = sampler.select_samples(X_unlabelled)
# Evaluating performance
accuracies.append(model.score(X_test, y_test))
# Updating the labeled and unlabeled pool
X_labelled = np.concatenate([X_labelled, selected])
# The selected samples are sent to be labeled as y_selected
y_labelled = np.concatenate([y_labelled, y_selected])
```
Here it is important to note that contrary to the beautiful learning curves from the literature or our documentation, in this setting
it can be non-monotonic when using small sample sizes ¯\_(ツ)_/¯.
## Yet another active learning package?
Several great active learning packages already exist, and you can find our take on them
[in this blog post](https://medium.com/data-from-the-trenches/a-proactive-look-at-active-learning-packages-8845fb6541e9).
As of today, cardinal is very similar to most of them, so why adding a new package to the ecosystem?
Our goal in cardinal is to grant maximum control to the user in a real-life setting. In cardinal, we aim not at providing
the latest and trendiest methods but simple methods that have been proven useful in a wide variety of cases. We have for
example decided to propose the recent Zdhanov's Diverse Mini-Batch Active Learning method because it relies a clustering
which is an idea already evoked in reference active learning papers (Xu2007), it is based on the well known KMeans
algorithm, and [we were able to replicate most of the findings in small and big datasets](https://medium.com/data-from-the-trenches/diverse-mini-batch-active-learning-a-reproduction-exercise-2396cfee61df).
In the future, we aim at addressing problems that are not covered, as far as we know, by other packages:
* **Varying batch size.** Most of other packages always assume that the batch size is the same across all iterations
which contradicts our experience on the matter. We are currently working on metrics designed to provide the
best insights even though the batch size changes during the experiment.
* **Mixing of several methods.** Active learning methods most often consists in getting the most out of diverse
sources of information. Several recent papers use a combination of
[semi-supervision](https://medium.com/data-from-the-trenches/re-discovering-semi-supervised-learning-a18bb46116e3)
and self-training. We want to enable this in our package.
## Installation
### Dependencies
cardinal depends on:
- Python >= 3.5
- NumPy >= 1.11
- SciPy >= 0.19
- scikit-learn >= 0.19 (optional)
- matplotlib >= 2.0 (optional)
- apricot-select >= 0.5.0 (optional)
Additional features are available in cardinal through different options:
* `sklearn` requires scikit-learn and provides a KMeans based sampler and a Batch method
* `submodular` requires apricot-select and scikit-learn. It allows to use a query sampler
based on a submodular facility location problem solver.
* `examples` requires scikit-learn, apricot-select, and matplotlib. It provides plotting
abilities and all the packages necessary to run the examples.
* `all` includes all of the above.
### Installing with pip
The easiest way to install cardinal is to use `pip`. For a vanilla install, simply type:
pip install -U cardinal
Optional dependencies are also handled by `pip` in the following way:
pip install -U 'cardinal[option]'
*option* can be one of:
- *sklearn* to enable scikit-learn related samplers such as clustering based ones
- *submodular* to install apricot-select to run the submodular sampler
- *examples* to install all required dependencies to run the examples
- *doc* to install the required dependencies to generate the sphinx-based documentation
- *all* to install all of the above
## Contributing
Contributions are welcome. Check out our [contributing guidelines](CONTRIBUTING.md).

